Yahoo Query Language (YQL)
Yahoo Query Language (YQL)
Using the YQL service is one way to request data from an external server and to overcome the cross-domain restrictions.
We can send a query to YQL which requests the data from the remote server and immediately sends the result, in the desired format, back to our application.
We can use the popular JS library jQuery to send an asynchronous HTTP request to YQL. You may not have used the jQuery libary yet, but it is required by the front-end framework Bootstrap. Therefore, it was included in most of our templates.
jQuery
jQuery is the most popular JS library and aims to simplify programming with JavaScript by providing many useful functions for DOM manipulation, event handling, animation and AJAX requests. Basically, it is a single JS file that should be included before your JS code.
Download: http://code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.min.js
<script src="js/jquery.min.js"></script>
Request data from Divvy Bikes with YQL:
// Webpage that returns JSON data
var url = 'https://www.divvybikes.com/stations/json';
// Build YQL query (request whole JSON feed from the given url)
var yql = 'http://query.yahooapis.com/v1/public/yql?q='
+ encodeURIComponent('SELECT * FROM json WHERE url="' + url + '"')
+ '&format=json&callback=?';
// Send an asynchronous HTTP request with jQuery
$.getJSON(yql, function(jsonData){
console.log(jsonData);
});
API response received over intermediary proxy:
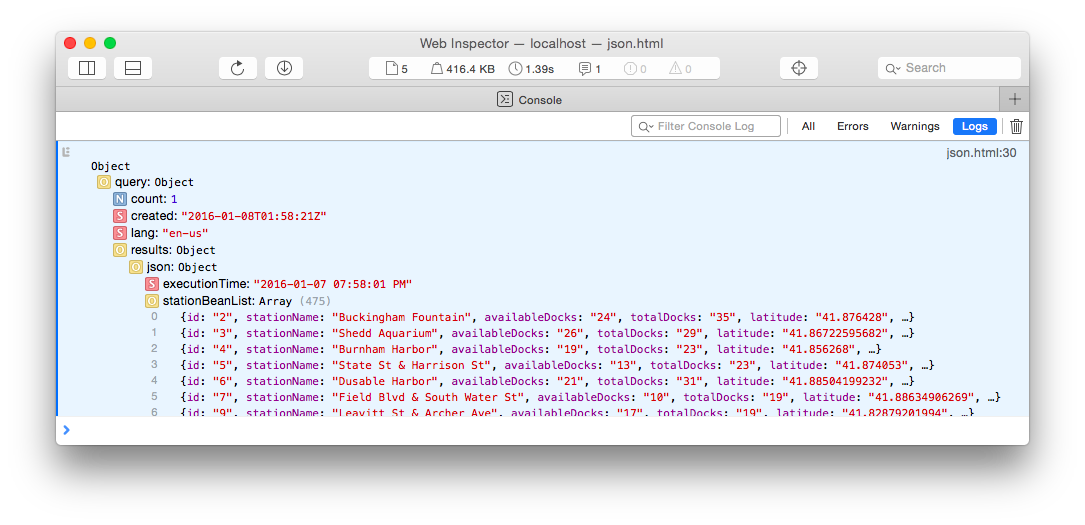
As you can see in the screenshot, the web service returned the requested list of bike sharing stations in Chicago. The data is deeply nested and contains additional information which is not necessarily needed, but fortunately it is in JSON format and you can easily traverse the tree by using the dot-notation:
// Get array with stations (JSON objects)
var stations = jsonData.query.results.json.stationBeanList;
Another advantage of using YQL is that you can choose between different formats. For example, if an API provides the data only as XML, it is difficult to transform it to the more convenient JSON format. You would need another JS library for the conversion. But in our case you just need to define the format parameter in the YQL query:
// XML to JSON
var yql = 'http://query.yahooapis.com/v1/public/yql?q='
+ encodeURIComponent('SELECT * FROM xml WHERE url="' + url + '"')
+ '&format=json&callback=?';
The example above was a use case for accessing dynamic data from an external web server. Other web services/data APIs might differ in that you (a) might have to deal with other data formats, or (b) have to append an API-key to the URL to get access to the server. But now you should have a general idea of API requests and how they differ from loading static datasets from an Open Data website.
